How to Build Real-Time Applications with Edge Computing
Introduction to Real-Time Applications and Edge Computing
Real-time applications are becoming a normal part of how businesses operate today. These applications react instantly to data, whether it’s a delivery status update, a live video feed, or a machine alert in a factory. Users expect quick responses, accurate updates, and smooth performance at all times.
Edge computing plays a key role in making this possible. Instead of sending all data to a central cloud server, edge computing processes data closer to where it is created, such as sensors, devices, or local servers. This reduces delays and helps applications respond more quickly to events.
In this article, we will explain how edge computing supports real-time applications, the technology behind it, and how businesses can start building edge-based systems. We’ll also cover practical use cases, challenges, and best practices to help you understand whether edge computing is the right choice for your application.
What Edge Computing Means for Real-Time Systems
Edge computing changes where and how data is handled. In traditional setups, data travels from devices to a central cloud server for processing. This travel takes time and can slow down applications that need instant responses. Edge computing solves this by handling data close to the source, such as on local servers, gateways, or even on the device itself.
For real-time systems, this approach makes a big difference. When data is processed nearby, applications can react immediately. A traffic camera can detect congestion and update signals without waiting for cloud instructions. A medical device can alert staff the moment a reading changes. A retail system can update stock levels the second an item is scanned.
Edge computing also reduces dependency on constant internet connectivity. If a connection drops, edge-based systems can keep working locally. Data can sync with the cloud later when the connection is stable. This is important for locations like factories, warehouses, remote sites, or moving vehicles.
Another key aspect is control. With edge computing, businesses decide what data stays local and what moves to the cloud. Sensitive information can be processed nearby, while summary data or insights are sent to central systems. This supports better privacy handling and keeps systems responsive during high data loads.
In short, edge computing helps real-time systems react quickly, stay reliable during network issues, and handle data in a smarter way by keeping critical processing close to where events happen.
Market Statistics and Trends for Edge Computing
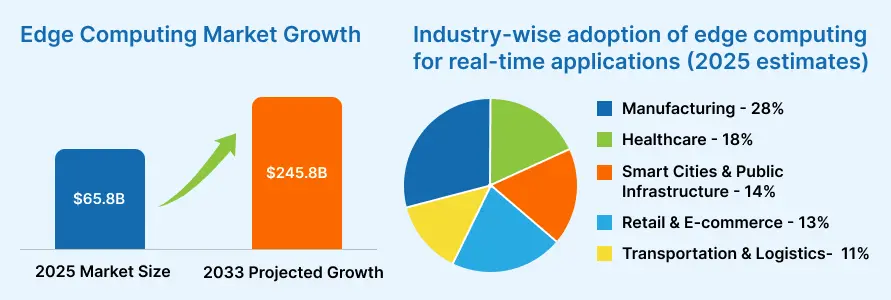
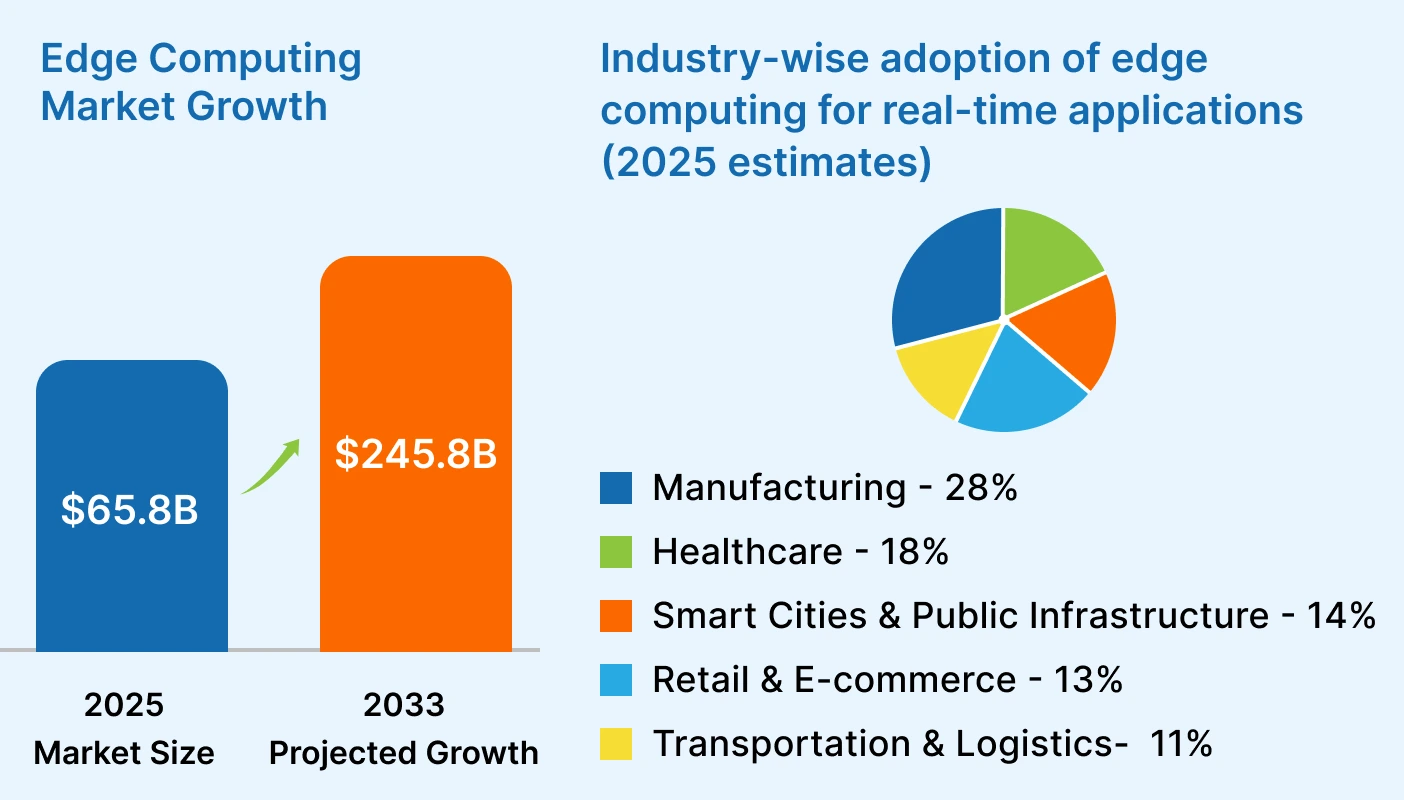
Edge Computing is becoming a major part of how businesses handle real-time data and application performance. The market growth shows that more companies are adopting edge technologies to support digital services.
Key Components of an Edge Computing Architecture

Building real-time applications with edge computing requires a clear understanding of the main parts involved. Each component plays a role in how data is collected, processed, and shared.
 Edge devices
Edge devices
These are the sources of data. Examples include sensors, cameras, IoT devices, point-ofsale systems, and industrial machines. They collect data continuously and send it for processing.
 Edge nodes or gateways
Edge nodes or gateways
Edge nodes sit close to the devices and handle data processing locally. They can be small servers, industrial gateways, or even powerful routers. These nodes filter, analyze, and act on data without sending everything to the cloud.
 Local processing and storage
Local processing and storage
Real-time decisions happen at this layer. Data is processed instantly and stored for short periods. This helps applications respond quickly and reduces the amount of data sent over the network.
 Cloud integration layer
Cloud integration layer
The cloud still plays an important role. It stores long-term data, supports analytics, and allows centralized management. Edge systems sync important data with the cloud when needed.
 Connectivity and networking
Connectivity and networking
Reliable communication connects devices, edge nodes, and cloud services. This can include wired networks, Wi-Fi, private networks, or cellular connections depending on the use case.
 Management and monitoring tools
Management and monitoring tools
These tools help teams monitor performance, update software, manage devices, and detect issues. Central dashboards provide visibility across all edge locations.
Together, these components form a flexible system that supports real-time processing while keeping long-term data and control centralized.
Common Use Cases for Real-Time Edge Applications
Edge computing supports many real-time applications across different industries. By processing data closer to where it is created, businesses can respond instantly to events and keep systems running smoothly.
How Edge Computing Improves Application Response Time

Real-time applications depend on quick reactions. Even small delays can affect user experience or system reliability. Edge computing improves response time by changing how and where data is processed.
 Manufacturing and industrial monitoring
Manufacturing and industrial monitoring
Real-time applications depend on quick reactions. Even small delays can affect user experience or system reliability. Edge computing improves response time by changing how and where data is processed.
 Processing closer to the source
Processing closer to the source
When data is handled near the device that creates it, there is less distance to travel. This reduces the time spent sending data back and forth to a central server. Applications can react almost instantly to changes.
 Reduced network congestion
Reduced network congestion
Sending all data to the cloud can overload networks, especially when many devices are active. Edge computing filters and processes data locally, so only important information is sent to the cloud. This keeps networks stable and responses consistent.
 Local decision-making
Local decision-making
Edge systems can take action without waiting for cloud instructions. For example, a machine can shut down when it detects a fault, or a camera system can trigger an alert the moment it sees unusual activity.
 Stable performance during connectivity issues
Stable performance during connectivity issues
If internet access becomes slow or unavailable, edge-based applications continue working locally. This avoids interruptions and keeps real-time systems running when they are needed most.
 Better user experience
Better user experience
Users notice faster updates, smoother interactions, and fewer delays. Whether it is a live dashboard or an automated system, edge computing supports a more responsive application flow.
By handling data locally and reducing reliance on distant servers, edge computing helps real-time applications respond quickly and stay dependable.
Technology Stack Needed for Edge-Based Applications

Building real-time applications with edge computing requires the right mix of hardware, software, and platforms. The stack should support fast processing, reliable communication, and easy management across multiple locations.
 Edge hardware
Edge hardware
This includes devices like industrial gateways, local servers, embedded systems, and smart sensors. The hardware should be powerful enough to process data locally and stable enough to run continuously.
 Operating systems and edge platforms
Operating systems and edge platforms
Lightweight operating systems are commonly used at the edge. These systems are designed to run on limited resources while supporting secure and stable operations. Some platforms also help manage edge devices remotely.
 Application frameworks and runtimes
Application frameworks and runtimes
Edge applications often use container-based frameworks to keep deployments consistent. Containers allow developers to package applications with all dependencies, making updates and scaling easier across many edge locations.
 Data processing and messaging tools
Data processing and messaging tools
Real-time systems rely on tools that handle streaming data and event-based communication. Message brokers and data pipelines help move data between devices, edge nodes, and the cloud.
 Cloud services for coordination
Cloud services for coordination
While processing happens locally, cloud services support monitoring, logging, long-term storage, and analytics. The cloud also helps manage configurations and updates for edge deployments.
 Security tools
Security tools
Security is part of the stack. This includes device authentication, encrypted communication, access controls, and monitoring tools to detect unusual activity.
Choosing the right technology stack depends on the use case, data volume, and location requirements. A well-planned stack helps edge applications stay reliable and easier to maintain.
Data Processing and Security at the Edge
Data processing at the edge focuses on handling information as close to its source as possible. This approach helps real-time applications react quickly while keeping sensitive data under better control.
Challenges in Building Real-Time Edge Applications
While edge computing brings many benefits, building real-time applications at the edge also comes with challenges. Understanding these early helps teams plan better and avoid issues during development and deployment.
 Device management at scale
Device management at scale
Edge applications often run across many devices in different locations. Managing updates, monitoring health, and keeping configurations consistent can become complex without the right tools.
 Limited computing resources
Limited computing resources
Edge devices usually have less processing power and storage compared to cloud servers. Applications must be designed to work within these limits while still handling real-time workloads.
 Security risks
Security risks
Edge devices are often placed in remote or public locations. This increases the risk of physical tampering or unauthorized access. Strong security practices are essential to protect data and systems.
 Data consistency and synchronization
Data consistency and synchronization
When data is processed locally, keeping it in sync with central systems can be challenging. Teams need clear rules on what data stays local and what gets shared with the cloud.
 Network variability
Network variability
Edge systems may operate in environments with unstable or slow connectivity. Applications must be able to handle network interruptions without losing critical data.
 Testing and debugging
Testing and debugging
Testing real-time behavior across distributed edge locations can be difficult. Issues may only appear under specific conditions, making troubleshooting more time-consuming.
Addressing these challenges requires careful architecture planning, reliable management tools, and ongoing monitoring.
Best Practices for Edge Application Development
Building real-time applications with edge computing works best when development follows clear and practical guidelines. These best practices help teams create stable systems that are easier to manage and scale.
 Design for local processing first
Design for local processing first
Start by deciding what data must be processed immediately at the edge. Keep timesensitive logic close to devices and move only useful data to the cloud. This keeps response times consistent.
 Keep applications lightweight
Keep applications lightweight
Edge devices have limited resources. Use simple services, small containers, and optimized code so applications run smoothly without overloading hardware.
 Use modular architecture
Use modular architecture
Break applications into smaller components that can be updated or replaced independently. This makes maintenance easier and reduces downtime during updates.
 Plan for offline operation
Plan for offline operation
Edge applications should continue working even when connectivity is weak or unavailable. Store data locally and sync it with central systems once the connection is restored.
 Automate deployment and updates
Automate deployment and updates
Managing many edge locations manually is risky. Use centralized tools to deploy updates, monitor device health, and apply patches across all locations.
 Build security into every layer
Build security into every layer
Secure devices, applications, and communication channels. Regular updates, strong authentication, and access controls should be part of the development process from day one.
 Test in real conditions
Test in real conditions
Test applications in environments that match real-world usage. This helps uncover issues related to network limits, hardware constraints, and response timing.
Following these practices helps teams build edge-based real-time applications that are stable, secure, and ready for long-term use.
Conclusion
Real-time applications are becoming essential for businesses that rely on fast data processing and instant responses. Edge computing makes this possible by bringing computation closer to users, devices, and data sources. It reduces latency, improves performance, lowers bandwidth costs, and supports better security and compliance.
As industries continue to adopt IoT, smart systems, and data-driven solutions, edge computing will play a key role in building scalable and responsive applications. Companies that plan early and choose the right architecture can gain a strong technical advantage and be ready for future growth.
At Brevity Technology Solutions, we help businesses design and build modern applications using edge computing, cloud platforms, and scalable architectures. Our team focuses on practical solutions that align with real business needs, not just technology trends.
Book a free consultation to discuss how edge computing can support your real-time application goals and digital strategy.
Related Post
-
F
-
A
-
Q
Edge computing processes data closer to where it is generated, such as devices, sensors, or local servers, instead of sending all data to a central cloud. This helps applications react faster.
By handling data locally, edge computing reduces delays, allowing instant responses for monitoring, alerts, transactions, or user interactions.
Yes. Most systems use a hybrid approach where the edge handles real-time tasks and the cloud stores data, supports analytics, and manages configurations.
Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, transportation, smart infrastructure, and media industries benefit due to their need for real-time processing and fast decision-making.
Start with a clear architecture, identify critical real-time tasks, choose suitable edge hardware, and use frameworks and tools for data processing and device management.
Use cases include industrial monitoring, retail point-of-sale systems, healthcare patient monitoring, fleet tracking, smart buildings, and video analytics.
Yes. Even small businesses can use edge computing for faster local processing, reduced cloud costs, and better reliability for real-time operations.
Use edge computing for tasks that need real-time decisions, local data processing, or high reliability, while reserving cloud systems for analytics, storage, and management.
Yes. Simulators, local test environments, container platforms, and cloud-based edge services can help test real-time applications before deployment.
Yes. Edge systems can process data and make decisions locally, then sync with cloud servers when connectivity is restored.
Want to Scale
Your Business? Let’s Meet & Discuss!

CANADA
30 Eglinton Ave W Mississauga, Ontario L5R 3E7

INDIA
3rd floor Purusharth Plaza, Amin Marg, Rajkot, Gujarat. 360002
Get a Quote Now
Let's delve into a thorough understanding of your challenges and explore potential solutions together