Edge Computing for Real-Time Application Performance
Introduction
Cloud Computing has been at the center of digital transformation for more than a decade. But as user expectations rise, the need for faster data processing has become more important. Sending data to faraway data centers and waiting for a response can create delays, and these delays affect how well real-time applications perform.
Edge Computing has become a strong solution to this challenge. Instead of sending all data to a central location, it processes information closer to where it is collected. This approach makes applications faster, more reliable, and better prepared for situations where quick action is needed.
In this article, we’ll explore what edge computing is, why it’s becoming more important, and how it helps real-time applications perform better. We’ll also share industry statistics, practical benefits, and real-world examples to give you a full picture of its impact.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing is a way to process data close to where it is created instead of sending all information to a central cloud server. Devices like smartphones, IoT sensors, and local servers can handle some data processing on their own. This reduces delays and allows apps to respond quickly. It is very useful for things that need instant results, like smart factories, healthcare monitoring, and online games.
 How Edge Computing Works
How Edge Computing Works
- Edge Devices: These are the sources of data, such as IoT sensors, smart cameras, wearable devices, or mobile phones. They collect data from the environment or user interactions.
- Edge Servers: Local servers or mini data centers handle processing close to the devices. They analyze and filter data before sending only what is necessary to the cloud.
- Central Cloud: The cloud stores aggregated data or performs complex analytics that do not require immediate action. Bandwidth usage is reduced, and response times are faster by sending only necessary data to the cloud.
 How Edge Computing is Different from Traditional Cloud Computing
How Edge Computing is Different from Traditional Cloud Computing
- In traditional cloud computing, all data is sent to a central server. This can create delays and slow down real-time performance.
- Edge Computing handles much of the processing closer to the user or device. This reduces delays, makes responses faster, and allows applications to work well even when the internet connection is slow or unstable.
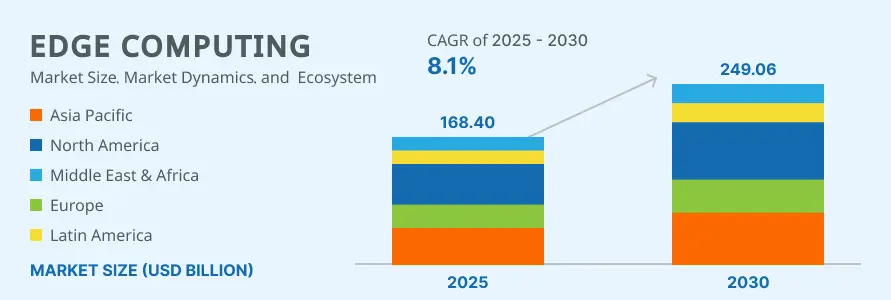
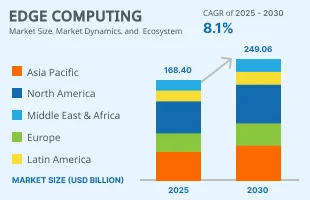
 Market Growth and Importance
Market Growth and Importance
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global edge computing market size was estimated at USD 168.40 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 249.06 billion by 2030, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2025 to 2030. This shows that businesses are using edge computing to handle more data and make apps faster.
Why Edge Computing Matters in 2025
Edge Computing has become a key technology for businesses that want to stay competitive in 2025. Processing data closer to where it is generated helps applications respond faster, handle more information, and adapt to changing needs. It also allows companies to build smarter systems that can make decisions in real time.
 Rapid Market Growth
Rapid Market Growth
The edge computing market is expanding quickly. More businesses are adopting edge solutions because they need faster applications, improved device performance, and realtime decision-making capabilities. With the number of connected devices increasing every year, companies can no longer rely solely on central cloud servers to process all data. Local processing through edge computing helps handle large amounts of information smoothly while keeping systems responsive.
 Better Real-Time Performance
Better Real-Time Performance
Applications that require instant responses benefit the most from edge computing. Processing data near the source reduces delays, or latency, which can make a big difference in industries like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, gaming, and smart city systems. For example, self-driving cars need to process sensor data immediately to avoid accidents. Similarly, industrial machines can detect faults and make corrections faster when data is handled locally. This speed can improve safety, productivity, and overall user experience.
 Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing helps businesses grow without creating bottlenecks in their systems. Companies can spread data processing across multiple edge devices and servers, reducing pressure on central cloud servers. This makes it easier to handle increasing amounts of data as the business expands. It also allows companies to add new devices, sensors, or applications without rebuilding their entire infrastructure. The flexibility of edge computing ensures that systems can evolve alongside the business.
 Stronger Security and Privacy
Stronger Security and Privacy
Handling sensitive information closer to the source improves security and privacy. Data does not need to travel long distances to reach a central server, which reduces the risk of interception or unauthorized access. This is especially important in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where protecting private data is critical. Companies can set up strict access controls, monitor data locally, and follow regulations more effectively when processing happens at the edge.


 Industry Adoption
Industry Adoption
Edge computing is already making a difference in many industries. Healthcare providers use it to monitor patients in real time and provides faster response to critical conditions. Manufacturing companies deploy edge solutions to track equipment performance, prevent downtime, and optimize production lines. Retailers use edge processing to improve inventory management and offer personalized experiences to customers in real time.
According to IDC, global spending on edge computing will grow at 13.8% reaching nearly $380 billion by 2028. This growth shows the increasing demand for real-time data handling and the widespread use of IoT devices in everyday business operations. As more industries will start using edge computing, companies that adopt these technologies early will have a competitive advantage in speed, reliability, and innovation.
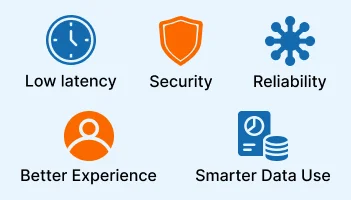
Key Benefits of Edge Computing for Real-Time Applications
Real-time applications depend on quick decisions and smooth performance. Even small delays can affect the user experience or bring errors. Edge computing helps solve these problems by processing data near the source, instead of sending everything to distant cloud servers.
Here are the main benefits:

Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
Edge Computing is already helping many industries work faster and handle data better. It allows companies to make decisions quickly, keep systems running smoothly, and respond to problems on time. Here’s how different sectors are using edge computing today:


 Manufacturing
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing world, even small delays can lead to big losses. Siemens uses edge computing on factory floors to keep track of machines and production lines in real time. Instead of sending data back and forth to distant data centers, they process it right where it’s collected.
This setup helps their teams spot unusual patterns, detect faults early, and fix problems before they grow. For example, if a machine starts overheating, the system can raise an alert on the spot, so technicians can take action quickly. This helps reduce waste, avoid long stoppages, and keep production running smoothly.
 Retail
Retail
The retail industry is a great example of how edge computing supports real-time decisionmaking and better customer experiences.
Walmart uses edge computing across its stores and warehouses to manage stock levels and track products more quickly. When data is processed near the shelves, staff can see which products are selling fast and restock them before they run out. This reduces empty shelves, improves store operations, and helps logistics teams plan better because they have live data.
Amazon Go takes it a step further with its cashierless shopping concept. These stores use hundreds of cameras and sensors to track what customers pick up. Edge computing processes this data directly inside the store, so customers can walk in, grab what they need, and leave without standing in line. The system automatically charges their account, making the entire shopping process fast and simple.
 Logistics
Logistics
DHL uses edge computing together with its SmartSensor devices to track shipments in real time. These sensors monitor things like temperature, humidity, location, and handling conditions as packages move through the supply chain.
Since the data is processed near where it’s collected, DHL teams get updates quickly. If something goes wrong, like a shipment getting delayed or sensitive goods being exposed to the wrong temperature, they can take action immediately. This helps protect goods and keeps customers better informed about their deliveries.
 Energy
Energy
GE Renewable Energy uses edge computing at wind farms to process data from turbines
By analyzing this data locally, GE can adjust the turbines immediately based on weather conditions and catch early signs of trouble. This keeps the turbines working well and helps technicians plan maintenance before bigger problems appear.
These real-world examples show how edge computing is already changing how businesses work in industries like manufacturing, retail, energy, and logistics. By moving data processing closer to where it happens, companies can react faster, cut delays, and give customers a smoother experience.
Challenges and Potential Solutions in Edge Computing
While edge computing brings many benefits, adopting it comes with some challenges. Understanding these early helps businesses plan better and avoid common mistakes.
 High Initial Costs
High Initial Costs
Setting up edge devices, local servers, and network infrastructure can be expensive.
Solution: Start small. Deploy edge computing in one part of your business first, like a single factory line or store, and expand gradually. Use cloud‑edge hybrid setups to reduce upfront costs.
 Complex Management
Complex Management
Managing multiple edge devices across different locations can be complicated.
Solution: Use centralized management software. This allows you to monitor and control all devices from one dashboard, making updates and maintenance easier.
 Data Security and Privacy
Data Security and Privacy
Although edge computing improves privacy by keeping data local, each edge device can become a potential entry point for attackers.
Solution: Implement strong encryption, access controls, and regular security updates. Train staff on cybersecurity best practices.
 Integration with Existing Systems
Integration with Existing Systems
Adding edge computing to existing apps and infrastructure can be tricky.
Solution: Plan a phased integration. Start by connecting edge devices to non-critical parts of your system and gradually expand. Use APIs and standard protocols for smoother integration.
 Connectivity Issues
Connectivity Issues
Even though edge reduces dependence on central servers, some level of connectivity is still required for updates or aggregated data transfer.
Solution: Use a hybrid setup that balances local processing with cloud support. Ensure reliable network connections and offline capabilities where possible.
 Limited Processing Power on Edge Devices
Limited Processing Power on Edge Devices
Edge devices may not have the same computing power as a cloud server.
Solution: Optimize applications to run smoothly on edge hardware. Offload heavy data analysis to the cloud when needed.
How to Integrate Edge Computing into Your Applications
With a clear plan, you can integrate edge benefits to your applications step by step.
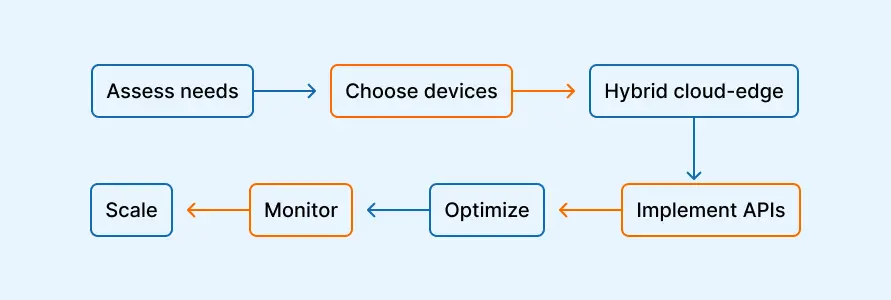
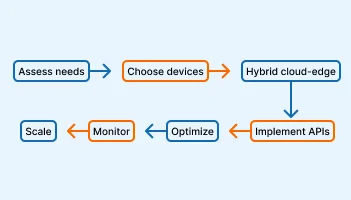
 Assess Your Needs
Assess Your Needs
Start by understanding which parts of your application need real-time processing.
- Example: A video streaming app may need edge computing to reduce buffering, while a reporting tool may not.
 Choose the Right Edge Devices
Choose the Right Edge Devices
Pick devices or local servers that match your processing needs
- IoT sensors for collecting data
- Local servers or mini data centers for processing
 Use a Hybrid Cloud-Edge Approach
Use a Hybrid Cloud-Edge Approach
Not all processing needs to happen at the edge. A hybrid setup balances workloads between the edge and central cloud.
- Heavy data analysis can still happen in the cloud
- Real-time decisions can be handled at the edge
 Implement APIs and Standard Protocols
Implement APIs and Standard Protocols
APIs help your edge devices communicate with cloud servers or other systems. Standard protocols make integration easier and reduce errors.
 Optimize Applications for Edge Hardware
Optimize Applications for Edge Hardware
Edge devices may have limited power compared to cloud servers.
- Simplify algorithms where possible
- Use lightweight data formats
- Offload heavy tasks to the cloud
 Monitor and Update Regularly
Monitor and Update Regularly
Once edge computing is running, monitor device performance and software. Regular updates help fix bugs, improve security, and maintain speed.
 Test Before Scaling
Test Before Scaling
Before rolling out edge computing across your whole business, test it in one location or with a smaller user base. Learn what works and adjust as needed.
Conclusion
Edge Computing is helping with how applications handle data, making them faster, smarter, and more reliable. By processing data closer to the source, businesses can deliver real-time experiences, protect sensitive information, and explore new use cases across industries like manufacturing, retail, logistics and energy.
At Brevity Technology Solutions, we help companies design and implement modern technology solutions, including edge computing, cloud integration, and real-time application optimization. If you want to explore how edge computing can improve your applications, book a free consultation call with our experts today!
Related Post
-
F
-
A
-
Q
Edge Computing is processing data closer to where it is created instead of sending everything to a central cloud server.
It reduces delays, allowing apps to respond quickly, which is helpful for gaming, healthcare, IoT, and smart factories.
Cloud Computing sends data to a central server for processing, while edge computing handles it locally, near the source.
Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, transportation, logistics, energy, and smart cities are some industries using it.
Yes. It reduces the risk of exposure during transmission by keeping sensitive data closer to its source.
Yes, startups can implement edge computing for parts of their operations that need realtime processing.
IoT sensors, mobile devices, local servers, mini data centers, and wearable devices.
Lower latency, faster responses, better reliability, smarter data usage, and improved security.
Some connectivity is needed for updates and cloud communication, but critical processing can happen offline
Yes. By processing data locally, only important data is sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth and storage costs.
Wearables and medical devices process data locally to provide instant alerts and protect patient privacy.
It’s a system where real-time data is processed at the edge while heavy data processing or storage happens in the cloud.
Yes. AI models can run locally on edge devices for real-time analysis and predictions.
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel and return a response. Edge computing can reduce this time on a maximum level.
Start with a small pilot project, test devices and applications, and gradually scale across operations. If you need guidance, Brevity Technology Solutions can guide you through planning, integration, and optimization. Book a free consultation call with our team to get started!
Want to Scale
Your Business? Let’s Meet & Discuss!

CANADA
30 Eglinton Ave W Mississauga, Ontario L5R 3E7

INDIA
3rd floor Purusharth Plaza, Amin Marg, Rajkot, Gujarat. 360002
Get a Quote Now
Let's delve into a thorough understanding of your challenges and explore potential solutions together


